[Abstract]:The preparation process of epoxy graft copolymerization of epichlorohydrin was studied. Through the analysis of various factors affecting the synthesis process, such as the ratio of water to gel, the amount of alkali added, and the time of alkaline hydrolysis, a preliminary study was made. A modification route different from the traditional modification process. The resulting modified bone glue adhesive has a low freezing point and high bond strength.
Key words: epichlorohydrin; modification; bone glue; adhesive
The chemical modification and physical modification of existing general-purpose polymers is an important and effective way to realize high-performance and multifunctional polymer materials. Bone glue is widely used in papermaking, printing, packaging, furniture, wood manufacturing, electroplating and other aspects with its excellent performance-to-price ratio. However, its own shortcomings, especially the gel state at room temperature, the need for heating and melting before use, poor storage stability seriously limit its popularization and application. At present, most of the modification methods used are starch and acrylic acid graft copolymerization with bone glue. Although the bond strength has been improved, the freezing point still cannot be reduced to below room temperature. In this paper, the defect of bone glue was discussed. A new process of bone glue modification was discussed. On this basis, a bone glue adhesive with liquid and high bond strength was successfully prepared at room temperature.
1, the experimental part
1.1 raw materials and specifications
Bone glue (technical grade); NaOH (chemical purity); Epichlorohydrin (analytic purity).
1.2 Experimental apparatus
NDJ4 rotary viscometer; infrared spectrometer (NOCOLET 60SXB FTIR); ordinary refrigerator; conventional organic synthesis instrument.
1.3 Preparation Process and Determination Analysis
1) Add 25g bone glue particles to a 250ml 3-neck flask, inject 25g water, and soak for 24h to fully swell the bone glue. The water bath was heated to 60° C., and 1.5 g NaOH was added to the mixture for 0.5 h at moderate speed. After cooling to 30° C., 2.5 g of epichlorohydrin was slowly added dropwise, and the mixture was stirred for 1.5 to 2 hours to obtain a yellow-brown viscous liquid.
2) Determination of the apparent viscosity of the modified bone glue binder. The apparent viscosity value was measured at (25±0.5°C) using an NDJ4 rotary viscometer.
3) Determination of the freezing point of modified bone glue binders. The prepared modified bone glue adhesive was formulated into a jar with a certain concentration of solution, and then the solution was placed in a refrigerator to observe the freezing point of the solution.
2. Results and Discussion
2.1 Reaction mechanism
Gelatin is a protein derivative obtained by simply hydrolyzing collagen. Its experimental formula is C102H151O39N31. The structural formula is generally represented by the following formula: 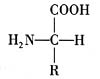
Most of the bone glue molecules consist of a simple polypeptide chain with an amino group at one end and a carboxyl group terminated at the other. Since -NH2 and -COOH are reactive groups, they associate with each other in an aqueous solution to form a reticulated insoluble solid point. The gel forms a gel. To break its gel state at room temperature, it is necessary to break the association between molecular chains. The bone glue is decomposed under alkaline conditions. By breaking the peptide bond, a suitable size of bone glue molecule is released and then grafted with epichlorohydrin to make  Grafting on the bone glue molecule to form a linear structure, on the one hand, the bone glue molecule chain grows and the binding property increases; on the other hand, the active group in the bone glue solution is reduced, and the association between the bone glue molecule chains and the formation of the gel are reduced. The trend is as follows:
Grafting on the bone glue molecule to form a linear structure, on the one hand, the bone glue molecule chain grows and the binding property increases; on the other hand, the active group in the bone glue solution is reduced, and the association between the bone glue molecule chains and the formation of the gel are reduced. The trend is as follows:

2.2 The effect of various factors on the apparent viscosity of the adhesive
2.2.1 Effect of Water/Binder Ratio on Apparent Viscosity
The relationship between the ratio of water added to the bone cement and the amount of bone glue and the apparent viscosity of the adhesive is shown in Table 1.

As can be seen from Table 1, the amount of water added to the swelling of the bone glue should not be too much nor too low, and the water-binder ratio should be 1:1. When the amount of water is too small, the bone glue particles cannot swell sufficiently, resulting in gelation in the subsequent reaction; when the amount of water is too much, although the subsequent reaction will not gel, the viscosity is very low, the initial viscosity of the glue is not good, and it is severe after 24 hours. Layered.
Plastic Storage Buckets/Baskets
Storage Basket,Plastic Product,Plastic Container
Plastic Storage Products Co., Ltd. , http://www.sensor-bin.com